Python Back-End Development – Handbook for Beginners

[ad_1]
Are you ready to dive into the world of Python back-end development? Whether you’re a beginner looking to learn the basics or an experienced developer wanting to upgrade your skills, this handbook is your ultimate guide.
Imagine being able to build full-featured web applications, handle large-scale data analysis, and create robust architecture designs using Python. With its vast ecosystem of libraries and built-in support for machine learning, Python has become the go-to programming language for back-end development.
In this guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about Python back-end development. We’ll discuss the role and responsibilities of a Python back-end developer, popular web frameworks, and the latest trends in the industry. We’ll also explore real-world applications and case studies, giving you practical insights into building efficient and scalable back-end systems.
Whether you’re interested in data-driven applications or API development, this tutorial will provide you with valuable knowledge and resources to excel in the world of Python back-end development. So, let’s get started.
Table Of Contents
- How to Launch Your Career as a Python Back-End Developer
- What is Python Back-end Development?
- Python Back-end Developer Skills
- Python Back-end Career Paths
- Recommended Python Libraries for Back-end Development
- How to Become a Python Back-end Developer
- Database Management in Python
- Security and Authentication in Back-end Development
- How to Prepare for a Back-end Python Developer Job
- Conclusion

Are you ready to embark on an exciting journey as a Python back-end developer? Python’s incredible versatility and power have made it a standout choice in the tech industry, especially for back-end development. This guide is your first step toward a flourishing career in this field.
Here are some of the topics we’ll cover in this handbook:
Python’s Critical Role in Back-End Development
Python, often thought of as a front-end language, is actually a powerhouse in back-end development. Its clear syntax, robust support, and expansive library ecosystem are pivotal in crafting efficient, scalable web applications.
So try to dispel any myths about Python’s performance limitations – advancements in interpreter technology and optimized libraries mean Python adeptly manages large code bases and numerous concurrent connections.
Career Pathways in Python Back-End Development
As a Python back-end developer, numerous career avenues await you. From junior developers to system architects, Python opens doors to diverse roles. Your expertise in Python can lead you to high-demand sectors, where your skills in data analysis, machine learning, and API development are highly valued.
Industry Demand and Career Growth
The demand for skilled Python back-end developers is soaring. Businesses across various industries seek professionals who can navigate Python’s capabilities to solve complex challenges. By learning Python, you position yourself at the forefront of an ever-growing job market.
Community Involvement and Networking
Engage with the Python community. Participate in forums, contribute to open-source projects, and network with fellow developers. This involvement is not just about learning – it’s about building relationships that can propel your career forward.
Structured Learning for Success
Begin your Python journey with a structured learning plan. Start with the basics – Python’s syntax and features – and utilize the wealth of online tutorials and resources available.
Then you can progress to exploring web frameworks like Django, Flask, and FastAPI. Each framework has its unique strengths and will equip you with the skills to build complex web applications.
How to Build a Personal Portfolio
Create a portfolio that showcases your Python projects, from simple to complex. These projects are proof of your skills and will serve as a cornerstone for your professional growth. They are not just demonstrations of your ability, but valuable learning experiences.
Seek Mentorship and Continuous Learning
Remember, becoming proficient in Python back-end development is a journey of continuous learning and practice. Seek mentorship from experienced developers and remain curious and motivated. Your path to becoming a Python back-end developer is filled with endless possibilities and opportunities for growth.
Embrace this journey with enthusiasm and determination, and watch as doors open in the dynamic world of Python back-end development.

Python allows you to create innovative backend solutions. This versatile language is swiftly becoming a go-to for developers seeking to create powerful server-side components for web applications.
But its simplicity and versatility are just the beginning. Python enables you to design solutions that make real-world impacts, bringing efficiency and innovation to various industries.
The Expansive Role of Python in Crafting Web Applications
When you write server-side code using Python, you’re directly handling requests from the front-end and engaging with databases and other resources.
The beauty of Python lies in its support for frameworks like Django, Flask, and FastAPI, simplifying the development of complex web applications. This is where you transform your code into functional, user-centric web applications.
How to Harness Python’s Advantages for Career Advancement
Python is renowned for its readability and clean syntax, making it an ideal language for both beginners and experienced developers. Its extensive library ecosystem equips you with tools to expedite development processes.
But there’s more – Python’s prowess in machine learning and data analysis opens up avenues in sophisticated back-end operations. This versatility allows for seamless integration with various databases, both SQL and NoSQL, catering to a wide array of applications.
As a career coach, I recommend leveraging these advantages by exploring real-world applications and community projects. This practical exposure not only enhances your skill set but also showcases your capabilities to potential employers.
How to Tackle Python’s Misconceptions with Confidence
Python, like any language, has its debates. Concerns about its performance, particularly in comparison to statically typed languages, do arise.
But Python’s dynamic nature and interpreted execution, when harnessed with efficient libraries and optimization techniques, are more than capable of powering large-scale web applications. Its multi-threading and asynchronous features allow handling numerous concurrent connections, a vital aspect of modern web development.
You can enhance your expertise in these areas through specialized training and community workshops, focusing on Python’s advanced features and performance optimization.
Stay Focused and Curious
As you embark on this journey, remember that Python back-end development is a continuous learning curve. Stay updated with the latest trends and advancements in Python. Engage in lifelong learning, explore new challenges, and actively seek opportunities for growth.
Building a strong foundation in Python, coupled with an eagerness to adapt and innovate, will set you apart in this dynamic field.
So as you can see, Python back-end development is not just about coding – it’s about creating, innovating, and constantly evolving. By embracing the versatility and power of Python and staying committed to continuous learning and skill enhancement, you are opening doors to a thriving career in technology.

Aspiring Python back-end developers need to acquire a specific set of skills and competencies to excel in their roles. These skills encompass a combination of programming knowledge, familiarity with web frameworks, database management, and an understanding of security and authentication protocols.
Proficiency in Python Programming
Being proficient in Python is an essential skill for any Python back-end developer. A deep understanding of the language’s syntax, features, and best practices allows developers to write efficient and reliable code.
Python’s simplicity, readability, and vast ecosystem of libraries make it a popular choice for back-end development.
If you want to get started learning Python, freeCodeCamp has a couple certifications just for you. Check out Scientific Computing with Python here, and Data Analysis with Python here.
There are also a number of great beginner-friendly Python courses on the freeCodeCamp YouTube channel – like this one from Harvard.
And if you want some great Python coding examples, check out these handbooks here and here.
Learn Python Web Frameworks
Python offers several powerful web frameworks that simplify the development process and provide built-in support for building full-featured web applications.
Popular frameworks like Django, Flask, and FastAPI offer different approaches to web development, allowing developers to choose the one that best suits their project’s requirements.
You can learn all about Django from the famous Dr. Chuck in this course on freeCodeCamp’s YouTube channel.
And you can learn about Flask by building an e-commerce app in this course.
And this handbook will teach you FastAPI basics while this course will solidify your knowledge.
Learn Database Management
Python back-end developers must have a good grasp of database management, including both SQL (Structured Query Language) and NoSQL (Non-relational) databases.
Understanding how to design database schemas, write efficient queries, and ensure data integrity is crucial for building robust back-end systems.
Here’s a course that’ll teach you SQL basics for data storage and retrieval.
And here’s a quick tutorial that teaches you how to use Python to read data from and write data to a table in SQL databases.
For NoSQL databases, here’s a full course that teaches you all about how they work.
Learn Security and Authentication
As back-end developers handle sensitive user data and interact with external systems, they must possess knowledge of security and authentication protocols. This includes understanding concepts like encryption, secure communication, user authentication, and authorization. Familiarity with frameworks and libraries that provide security features is also essential.
Here’s a helpful tutorial on web security in Django, and here’s a tutorial about setting up authentication in a Flask app. Hopefully these will give you some basic ideas and inspire you to learn more if you need to do so.
Developers who possess these skills will be well-equipped to tackle the challenges of back-end development using Python.
By continuously honing their skills and staying updated with the latest trends and best practices, Python back-end developers can deliver high-quality and secure web applications.

As a Python back-end developer, you have a wide range of career paths to choose from. The demand for skilled Python developers is on the rise, and there are numerous opportunities in various fields.
Here are some of the career paths you can explore:
Web Development
Web development is one of the most common career paths for Python back-end developers. You can work on building and maintaining websites, web applications, and content management systems.
With Python’s versatility and the availability of web frameworks like Django and Flask, you can create robust and scalable web solutions.
Data Analysis
Python is widely used for data analysis and manipulation. As a Python back-end developer, you can work with large datasets, perform statistical analysis, and create data visualizations. Tools like NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib are commonly used in this field.
Machine Learning
Python is the language of choice for machine learning and artificial intelligence. As a Python back-end developer, you can develop machine learning models, implement deep learning algorithms, and work on natural language processing projects. Libraries like TensorFlow and scikit-learn are popular for this purpose.
DevOps and Deployment
Python is also valuable in the DevOps field. You can work on automating deployment processes, managing infrastructure, and building scalable systems. With tools like Docker and Kubernetes, you can streamline the deployment and maintenance of applications.
Backend Architecture and Design
If you have a strong grasp of backend architecture and design principles, you can pursue a career as a backend architect or technical lead. You will be responsible for designing scalable, efficient, and secure backend systems and ensuring smooth integration with frontend components.
The salaries for Python back-end developers vary based on experience, location, and industry. But the average salary for Python professionals is quite competitive, with ample room for growth and advancement.
Remember, this is just a glimpse of the career paths available to Python back-end developers. With the continuous growth and evolution of technology, new opportunities are constantly emerging. Stay updated with the latest trends and technologies to make the most out of your career in Python back-end development.

When it comes to Python backend development, leveraging the right libraries can significantly streamline the development process and enhance the functionality of your web applications.
Here are five Python tools that can simplify and optimize your backend development workflow:
Flask
Flask is a micro web framework that offers simplicity and ease of use without sacrificing functionality. It provides a minimalistic syntax and focuses on the core features of web development, making it an excellent choice for small to medium-sized projects.
Flask’s modular design allows developers to add the necessary extensions to create a full-featured web application. It is highly extensible and beginner-friendly, making it a great library for developers getting started with Python backend development.
FastAPI
FastAPI is relatively new, but it’s rapidly gaining popularity as a high-performance web framework. It combines modern, asynchronous programming techniques with the simplicity and productivity of the Python language.
FastAPI leverages the power of type hints and automatic documentation generation, making it easier for developers to build robust and well-documented APIs. Its speed and efficiency make it an excellent choice for building scalable backend systems.
Django
Django is a widely used, batteries-included web framework that simplifies the process of building complex web applications. It provides built-in support for various functionalities, including authentication, database management, and URL routing.
Django’s robustness and scalability have made it a preferred choice for a wide range of applications, from basic websites to large-scale enterprise systems.
Tornado
Tornado is a popular open-source web framework that excels in handling high-performance, real-time web applications. Its non-blocking architecture makes it ideal for building scalable applications that require handling a large number of concurrent connections.
Tornado’s lightweight and efficient design, along with its support for long polling and websockets, makes it a valuable tool for developers working on real-time applications.
Pyramid
Pyramid is a powerful and flexible web framework that prioritizes simplicity and speed. It provides a solid foundation for building both small and large-scale web applications.
Pyramid follows the principle of “pay only for what you need,” allowing developers to choose and integrate various components according to their requirements.
With its extensive documentation and active community, Pyramid is a popular choice among Python developers.
By utilizing these libraries in your Python backend development projects, you can benefit from their extensive features and community support. Each library has its own strengths, so it’s essential to evaluate your specific project requirements and choose the one that best fits your needs.

Becoming a Python back-end developer requires a combination of technical skills, practical experience, and continuous learning. Here are some actionable steps and guidance to help you kickstart your journey:
Fortify Your Python Foundations
Embarking on your Python back-end development journey begins with a deep dive into Python’s fundamentals. Set specific, measurable goals to master Python’s syntax and core concepts.
For instance, aim to understand basic syntax within the first couple weeks, or complete a mini-project using object-oriented principles within a month.
Supplement your learning with practical exercises at the end of each session. These exercises reinforce theoretical knowledge and aid in retention.
It’s also a good idea to engage in peer review and collaboration by joining coding forums or local Python groups. This exposure can offer new perspectives and enhance your problem-solving skills, forming a solid foundation for your journey.
Expand Your Web Development Horizons
As you progress, broaden your understanding of web development essentials. While your focus may be on back-end development, a well-rounded knowledge of front-end technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is crucial.
Explore resources or short courses that offer a comprehensive overview of these front-end technologies. You can also analyze real-world applications to see how these technologies are applied in practice.
This approach provides a holistic view of web development, preparing you to create more integrated and efficient back-end systems.
Learn Python Web Frameworks
Venture further into Python’s powerful web frameworks, such as Django, Flask, and FastAPI that we discussed above. Each framework has its unique strengths, so consider undertaking a comparative project where you utilize different frameworks for the same application.
This practical experience will deepen your understanding of each framework’s capabilities.
Engage actively in community forums, workshops, and contribute to open-source projects related to these frameworks. Such community engagement is not only enriching but also keeps you abreast of the latest developments and best practices in Python web frameworks.
Learn Database Management
Database management is a critical aspect of back-end development. Familiarize yourself with both SQL and NoSQL databases – we’ll discuss these in more detail in subsequent chapters.
Hands-on projects involving the setup and management of databases will provide invaluable experience. Incorporate case studies of real-world database management scenarios to understand the challenges and best practices in this field. This knowledge is crucial for storing, retrieving, and manipulating data efficiently in your applications.
Create a Personal Portfolio
Building a personal portfolio is essential in showcasing your skills. Select projects that not only demonstrate your technical prowess but also align with your career aspirations.
For instance, if data science intrigues you, focus on projects that involve data analysis and manipulation. Regular portfolio reviews by mentors or peers can provide constructive feedback, helping you refine your portfolio to better reflect your capabilities and aspirations.
Go Through Certifications and Courses
Enhance your skills and professional standing by enrolling in relevant courses and obtaining certifications. Choose educational paths that align with your career goals, ensuring that your learning journey strategically builds towards your desired role. Customize your learning path to fit your personal learning style and pace, making your educational experience more effective and enjoyable.
Keep Pace with Industry Trends
Stay updated with the latest trends in Python back-end development. Seek mentorship from industry professionals who can provide insights into current industry trends and offer valuable career advice. Regularly subscribe to industry newsletters, listen to podcasts, and follow influencers in the Python development space to stay informed.
Your path to becoming a skilled Python back-end developer involves a combination of solid foundational learning, practical application, continuous education, and active community engagement. Each step should be approached with dedication and enthusiasm, keeping you inspired and informed as you explore the vast possibilities of Python and back-end development.
Now let’s get into some of the more nitty-gritty details of what it takes to work with Python on the back end.

Database management is a crucial aspect of building robust and efficient applications in Python. It involves effectively organizing and manipulating data to support various operations.
In this chapter, we will explore the definition and significance of database management and provide an overview of SQL and NoSQL databases in Python.
Database management refers to the process of organizing, storing, and retrieving data in a structured manner. It plays a vital role in ensuring data integrity, enabling efficient data access, and facilitating data analysis.
By effectively managing databases, developers can create scalable and reliable systems that support various business needs.
SQL vs. NoSQL: Making the Informed Choice
In the realm of databases, understanding the distinction between SQL and NoSQL is crucial.
SQL databases shine with their structured query language, offering unparalleled precision for applications that rely on complex queries and transactional integrity. They are the bedrock for scenarios demanding strict data consistency, detailed relationships, and clear schema definitions.
On the other hand, NoSQL databases bring flexibility to the table, catering to applications that deal with large volumes of unstructured data or need to scale rapidly. Their schema-less nature allows for quick adaptations and supports a variety of data models, including key-value, document, wide-column, and graph formats.
The decision between SQL and NoSQL hinges on the specific needs of your project. If your application requires meticulous data organization and complex transactions, SQL is the dependable choice. For projects that must scale dynamically or handle a diverse set of data structures, NoSQL offers the agility and scalability needed.
Choose wisely, focusing on the demands of your application and the data it will handle. Both SQL and NoSQL databases have their place in the technology landscape, each bringing strengths that, when matched with the right project requirements, can significantly enhance your application’s performance and scalability.
SQL Databases in Python
SQL databases play a crucial role in storing and managing data in Python applications. They provide a structured approach to data storage, utilizing tables with predefined schemas.
With SQL databases, you can efficiently organize and retrieve data, making them ideal for applications that require complex querying and relationships between data entities.
Let’s look at an example.
When working with SQL databases in Python, you can use libraries like sqlite3 and SQLAlchemy to connect to the database and perform operations.
For instance, you can establish a connection to an SQLite database using sqlite3.connect() and then execute SQL queries to retrieve and manipulate data.
Here, we’re creating a table called users to store user information:
import sqlite3
# Connect to the database
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
# Create a cursor object
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Execute SQL queries
cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM users")
users = cursor.fetchall()
# Print the results
for user in users:
print(user)
# Close the connection
conn.close()
Connecting to SQL databases using Python libraries like sqlite3 and SQLAlchemy
To connect to SQL databases in Python, you can leverage libraries such as sqlite3 and SQLAlchemy. These libraries provide convenient APIs to establish connections, execute queries, and handle database operations.
Designing database schemas for SQL databases
Designing an effective database schema is crucial for SQL databases. A well-designed schema ensures efficient data organization, optimal querying performance, and data integrity. When designing a schema, consider the relationships between different entities and define appropriate tables, columns, and constraints.
Writing efficient SQL queries and ensure data integrity
To maximize performance and ensure data integrity, it is important to write efficient SQL queries. Consider using indexes, optimizing joins, and using appropriate SQL clauses to retrieve the required data. You can also enforce data integrity by defining constraints, such as primary key and foreign key constraints.
By understanding SQL databases, connecting to them using libraries like sqlite3 and SQLAlchemy, designing effective schemas, and writing efficient queries, you can effectively manage data storage in your Python applications.
NoSQL Databases in Python
NoSQL databases provide a flexible and scalable approach to data storage, making them suitable for various use cases in Python.
One popular NoSQL database is MongoDB, which allows for storing data in a document format. This makes it ideal for scenarios where data structures may evolve or have varying attributes.
For example, let’s say you are working on a Python project that involves analyzing social media data. By using MongoDB and its document-oriented model, you can easily store and retrieve data such as user profiles, posts, and comments, without the need for a predefined schema. This flexibility allows for efficient handling of dynamic data.
Let’s look at an example. We can use the pymongo library to connect and interact with the database. Here’s an example of inserting a document into a collection called products:
from pymongo import MongoClient
# Connect to the MongoDB database
client = MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017/')
# Access the database
db = client['social_media']
# Access the collection for user profiles
profiles_collection = db['profiles']
# Insert a new user profile document
profile = {
'username': 'john_doe',
'name': 'John Doe',
'followers': 1000
}
profiles_collection.insert_one(profile)
# Retrieve all user profiles
profiles = profiles_collection.find()
# Print the user profiles
for profile in profiles:
print(profile)
# Close the connection
client.close()
How Do NoSQL Databases Work?
NoSQL databases represent a broad class of database management systems that differ significantly from traditional relational database systems (RDBMS). These databases are designed to excel in areas where relational databases might struggle, particularly in handling large volumes of unstructured or semi-structured data, accommodating rapid scaling, and facilitating agile development practices that require schema flexibility.
Unlike SQL databases that store data in tables with predefined schemas, NoSQL databases use a variety of data models, including key-value pairs, documents, wide-column stores, and graphs. This diversity allows them to store and manage data in a format that is closer to the data’s native structure, enhancing the efficiency of data retrieval and manipulation.
As a result, NoSQL databases have become a popular choice for developing modern applications in web, mobile, and IoT domains, where the ability to handle vast amounts of varied data types and structures quickly is paramount.
One of the key strengths of NoSQL databases is their scalability. They are designed to scale out by distributing data across multiple servers, often in a distributed system environment. This contrasts with the scale-up approach of traditional RDBMS, where a single server’s resources are increased.
NoSQL’s distributed architecture enables horizontal scalability, improving performance and availability while managing the cost implications of dealing with big data.
Furthermore, NoSQL databases often provide flexible schemas, allowing developers to alter the data structure as the application evolves without needing to predefine the schema. This flexibility facilitates rapid development and iteration, making NoSQL databases particularly suited to projects with evolving data models or projects that must go to market quickly.
Connecting to NoSQL Databases with Python Libraries
Diving into NoSQL databases with Python opens a world of possibilities for handling diverse data types and structures. Python offers a variety of libraries tailored to different NoSQL databases, such as pymongo for MongoDB, redis-py for Redis, and cassandra-driver for Cassandra. Each library simplifies the connection process, enabling developers to interact with the database using Pythonic conventions.
Establishing a connection typically involves specifying the database URI and credentials, after which you can perform CRUD operations seamlessly. This step is crucial for leveraging the full potential of NoSQL databases in your Python applications, providing the flexibility to work with data as your project requires.
Designing Data Models for NoSQL Databases
When it comes to NoSQL databases, designing effective data models is a game-changer. Unlike SQL databases that follow a strict schema, NoSQL databases allow for a more flexible data structure, which can be optimized based on the specific use case.
Whether you’re working with document, key-value, wide-column, or graph databases, understanding the strengths and use cases of each type enables you to design data models that enhance performance and scalability.
This involves considering how data is accessed and manipulated, ensuring that the model supports efficient querying and updates. Effective data modeling in NoSQL databases paves the way for building dynamic applications that can adapt to changing requirements.
Writing Effective Queries in NoSQL Databases
To tap into the power of NoSQL databases, writing effective queries is key. Each type of NoSQL database offers unique querying capabilities, from MongoDB’s BSON-based syntax to the graph traversal languages of graph databases. Mastering these query languages allows developers to retrieve, update, and manipulate data efficiently.
The goal is to optimize query performance without compromising the flexibility and scalability that NoSQL databases provide. This requires a deep understanding of the database’s indexing capabilities and query execution plan, enabling developers to write queries that are both powerful and efficient.
Ensuring Data Integrity in NoSQL Databases
Maintaining data integrity in NoSQL databases presents unique challenges, given their schema-less nature and eventual consistency model. But strategies such as implementing application-level validation, using database features for atomic operations, and understanding the database’s consistency guarantees can mitigate these challenges.
It’s also important to consider transaction support, where needed, to ensure that data remains consistent across operations. By carefully planning for data integrity, you can build NoSQL-backed applications that are not only scalable and flexible but also reliable, meeting the demands of modern web and mobile applications.
How to design database schemas for NoSQL databases and their types (Document, Key-Value, and so on)
When designing a database schema for a NoSQL database, it is crucial to consider the specific type of NoSQL database you are working with. For example, if you are using a document-oriented database like MongoDB, you can structure your data as JSON-like documents.
Let’s say you are developing a Python application for an e-commerce platform. With a document-oriented NoSQL database, you can design your schema to represent products as documents, including attributes like name, price, and category. This schema flexibility allows for easy expansion and modification of data structures as your application evolves.
How to perform CRUD operations with NoSQL databases in Python
CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) are fundamental tasks when working with databases. In Python, you can perform these operations with NoSQL databases using libraries like pymongo.
For example, imagine you are building a sentiment analysis application in Python, and you are using a NoSQL database to store user reviews. With pymongo, you can easily create a new document to store a user’s review, retrieve reviews based on specific criteria, update review ratings, or delete unwanted reviews. This flexibility in performing CRUD operations allows you to effectively manage and manipulate data in your NoSQL database.
Database Schema Design
A well-designed database schema is of utmost importance in Python frontend and backend development, NLP, data science, and machine learning. It provides the foundation for efficient data organization and retrieval.
Let’s explore techniques for creating effective database schemas and tools for visualizing and documenting them.
When designing a database schema, consider the specific requirements of your application.
Start by identifying the entities and relationships that need to be represented. For example, in an e-commerce application, you may have entities such as customers, products, and orders. Each entity can be represented as a table with columns representing specific attributes.
Next, define the relationships between the entities using foreign keys. For instance, an order can be associated with a customer and contain multiple products. By defining these relationships, you ensure data consistency and enable efficient querying.
To create a well-designed database schema, it is essential to follow best practices such as normalizing the data. This involves breaking down data into smaller, logical units to minimize redundancy and improve data integrity.
For example, instead of storing customer addresses directly in the orders table, you can create a separate table for addresses and link them using foreign keys.
You should also consider the performance implications of your schema design. Indexing key columns can significantly improve query performance by allowing the database to quickly locate specific data. Be mindful of the trade-off between the number of indexes and the overhead they introduce during data modification operations.
When it comes to visualizing and documenting the database schema, there are various tools available. One popular tool is MySQL Workbench, which provides a graphical interface for designing and visualizing database schemas. Another useful tool is Lucidchart, which allows you to create professional-looking entity-relationship diagrams.
Here’s an example of using the MySQL Workbench tool to design a database schema:
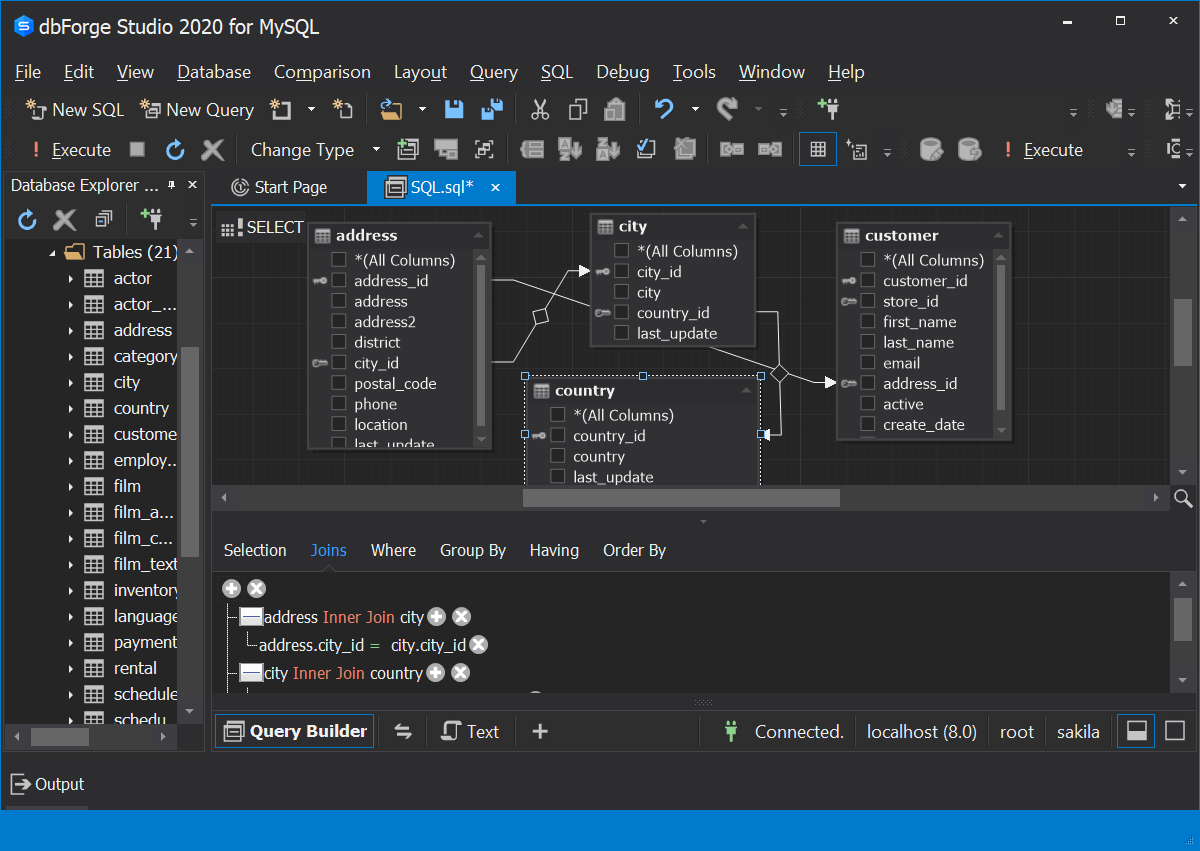
Let’s illustrate these concepts with an example. Suppose we are building a blog application, and we need to design the database schema.
We can start by identifying the entities: authors, posts, and comments. The authors table can have columns like id, name, and email. The posts table can have columns like id, title, content, and author_id (a foreign key referencing the authors table). The comments table can have columns like id, content, post_id (a foreign key referencing the posts table), and author_id (a foreign key referencing the authors table).
import sqlite3
# Connect to the database
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
# Create a cursor object
cursor = conn.cursor()
# Create the tables
cursor.execute('''CREATE TABLE authors
(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT, email TEXT)''')
cursor.execute('''CREATE TABLE posts
(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, title TEXT, content TEXT, author_id INTEGER,
FOREIGN KEY(author_id) REFERENCES authors(id))''')
cursor.execute('''CREATE TABLE comments
(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY, content TEXT, post_id INTEGER, author_id INTEGER,
FOREIGN KEY(post_id) REFERENCES posts(id),
FOREIGN KEY(author_id) REFERENCES authors(id))''')
# Close the connection
conn.close()
By following these techniques and utilizing appropriate tools, you can create a well-designed database schema that supports efficient data management and retrieval in Python applications. Remember to constantly evaluate and refine your schema as your application evolves and new requirements arise.
Query Optimization and Performance
Optimizing SQL queries for better performance is essential in Python frontend and backend development, NLP, data science, and machine learning. Here are some tips to improve query performance:
Efficiently use indexes
Indexes help speed up query execution by allowing the database to quickly locate specific data. Identify frequently accessed columns and create indexes on them. For example, if a column is frequently used in WHERE clauses or JOIN conditions, consider creating an index on that column.
Example: Suppose we have a table called “products” with a column “name” frequently used in search queries. We can create an index on the “name” column to improve search performance.
import sqlite3
# Create an index on the "name" column
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('CREATE INDEX idx_products_name ON products(name)')
conn.close()
Optimize JOIN operations
JOIN operations can be resource-intensive. To enhance performance, minimize the number of JOIN operations and optimize the join conditions. Avoid unnecessary JOINs and use appropriate join types (e.g., INNER JOIN, LEFT JOIN) based on the relationship between tables.
Example: If we have two tables, “customers” and “orders,” with a one-to-many relationship, use INNER JOIN to retrieve customers who have placed orders.
import sqlite3
# Retrieve customers who have placed orders using INNER JOIN
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('SELECT customers.name, orders.order_number FROM customers INNER JOIN orders ON customers.id = orders.customer_id')
result = cursor.fetchall()
conn.close()
Use appropriate SQL clauses
Utilize SQL clauses like WHERE, GROUP BY, and HAVING to filter and aggregate data efficiently. Restrict the amount of data returned by applying filters early in the query.
Example: When retrieving customer data, use WHERE clauses to filter by specific criteria, such as age or location.
import sqlite3
# Retrieve customers older than 18 years
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('SELECT * FROM customers WHERE age > 18')
result = cursor.fetchall()
conn.close()
Minimize data retrieval
Only retrieve the necessary columns and rows to reduce the amount of data transferred between the database and application. Avoid using SELECT * and limit the result set to the required data.
Example: Instead of retrieving all columns from the “users” table, specify only the required columns, such as name and email.
import sqlite3
# Retrieve only the required columns from the "users" table
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('SELECT name, email FROM users')
result = cursor.fetchall()
conn.close()
Use Execution Plans
Analyzing and tuning database queries using execution plans is another valuable technique. Execution plans provide insights into how the database executes queries and can help identify performance bottlenecks. Examine the execution plan to ensure optimal query execution and identify areas for optimization.
Example: Use the EXPLAIN keyword in SQL to obtain the execution plan of a query and analyze it to identify potential performance improvements.
import sqlite3
# Retrieve the execution plan of a query
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM products WHERE price > 100')
result = cursor.fetchall()
conn.close()
Best practices for database indexing and transaction management are crucial to ensure data integrity and optimize performance:
Identify appropriate columns for indexing
Select columns that are frequently used in WHERE clauses, JOIN conditions, and ORDER BY clauses. Avoid over-indexing, as it can introduce overhead during data modification operations.
Example: If we often search for products by category, create an index on the “category” column to speed up these queries.
import sqlite3
# Create an index on the "category" column
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('CREATE INDEX idx_products_category ON products(category)')
conn.close()
Manage transactions effectively
Use transactions to group multiple database operations into a single logical unit. This ensures data consistency and allows for rollback in case of errors.
Example: When updating customer information, encapsulate the update operation within a transaction to guarantee that all changes are either committed or rolled back.
import sqlite3
# Update customer information within a transaction
conn = sqlite3.connect('example.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute('BEGIN')
cursor.execute('UPDATE customers SET email = ? WHERE id = ?', ('[email protected]', 1))
cursor.execute('COMMIT')
conn.close()
By following these practices, you can optimize SQL queries, analyze and tune execution plans, and implement effective database indexing and transaction management in Python frontend and backend development, NLP, data science, and machine learning projects.
Advanced Topics in Database Management
Exploring database sharding, replication, and clustering is essential for Python backend development. These strategies address scalability challenges by distributing data across multiple servers.
Sharding involves partitioning a database into smaller pieces, allowing for horizontal scaling. Replication creates multiple copies of a database to improve read performance and ensure data availability. Clustering connects servers to work as a single system, providing high availability and load balancing.
These strategies enable Python backend developers to build scalable, high-performance systems that can handle growing data requirements.
import pymongo
# Connect to the MongoDB database
client = pymongo.MongoClient('mongodb://localhost:27017/')
# Enable sharding for the database
admin_db = client.admin
admin_db.command('enableSharding', 'my_database')
# Shard the collection based on a specific criterion
admin_db.command('shardCollection', 'my_database.my_collection', key={'user_id': 1})
# Close the connection
client.close()
Databases are crucial for Python backend development, especially in big data and real-time applications. Python’s simplicity and extensive library ecosystem make it an ideal choice for handling large amounts of data and enabling real-time data processing.
With databases, developers can efficiently manage and query big datasets, extract insights, and handle real-time data streams. Python’s integration with databases like Hadoop, Apache Spark, and PostgreSQL, as well as real-time data processing frameworks like Apache Kafka and Redis, empowers developers to build scalable and responsive applications.
By understanding the role of databases in big data and real-time applications, Python backend developers can effectively handle data challenges and build efficient and reliable applications.
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
# Create a SparkSession
spark = SparkSession.builder \\\\
.appName('Real-Time NLP Analysis') \\\\
.getOrCreate()
# Read data from a big data source, such as Apache Kafka
df = spark \\\\
.readStream \\\\
.format('kafka') \\\\
.option('kafka.bootstrap.servers', 'localhost:9092') \\\\
.option('subscribe', 'my_topic') \\\\
.load()
# Perform NLP analysis on the real-time data
# ...
# Write the results to a database for further analysis
df.write \\\\
.format('database') \\\\
.option('url', 'jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/my_database') \\\\
.option('dbtable', 'nlp_results') \\\\
.mode('append') \\\\
.save()
# Stop the SparkSession
spark.stop()
Integrating Python applications with cloud-based database services is crucial for Python backend development. Cloud-based databases offer scalability, high availability, and easy management, making them ideal for handling the increasing demands of modern applications. By leveraging cloud-based databases, Python developers can focus on building robust and efficient backend systems without the need to manage infrastructure.
There are several benefits to using cloud-based database services in Python backend development.
First, they provide automatic backups and disaster recovery, ensuring data is protected and can be easily restored in case of any issues.
Second, these services offer built-in security features, such as encryption and access control, to protect sensitive data. Third, they enable seamless scalability, allowing applications to handle growing user bases and increasing data volumes without significant performance issues.
Cloud-based database services also provide built-in monitoring and analytics capabilities, giving you insights into the performance and usage of your applications. They also offer integration with other cloud services, such as serverless computing platforms and container orchestration tools, allowing you to build highly scalable and efficient application architectures.
Using cloud-based databases in Python backend development simplifies the deployment process. You can easily provision and configure database instances, manage database schemas, and perform backups and restores through simple APIs or web-based interfaces. This allows for faster development and deployment cycles, reducing time-to-market for new features and updates.
import boto3
# Connect to the Amazon RDS database
client = boto3.client('rds')
# Create a new database instance
client.create_db_instance(
DBInstanceIdentifier="my-instance",
Engine="mysql",
DBInstanceClass="db.t2.micro",
AllocatedStorage=10,
MasterUsername="admin",
MasterUserPassword='password'
)
# Connect to the database
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="my-instance.abc123.us-west-2.rds.amazonaws.com",
user="admin",
password='password',
database="my_database"
)
# Perform database operations
# ...
# Close the connection
conn.close()
By examining this example code, I hope you can better understand how to implement database sharding and how to leverage databases in big data and real-time applications. You should also understand how to integrate Python applications with cloud-based database services in Python frontend and backend development, NLP, data science, and machine learning projects.

Introduction to Security in Back-End Development
In back-end development, security is essential for protecting data integrity and confidentiality. Neglecting security can lead to serious issues like data breaches and loss of user trust. To prevent this, a security-first approach in the development process is vital.
Let’s briefly go over some key security practices with code examples.
User Authentication:
Implementing strong authentication methods, such as passwords, tokens, and multi-factor authentication, is crucial to prevent unauthorized access. For instance, multi-factor authentication adds an additional security layer beyond just passwords.
Here’s an example of implementing User Authentication in Python:
# Password-based authentication
def authenticate_user(username, password):
# Check if username and password match in the database
# Return True if authentication is successful, False otherwise
# Token-based authentication
def generate_token(user_id):
# Generate a unique token for the user
# Save the token in the database along with the user ID
# Return the generated token
def verify_token(token):
# Check if the token exists in the database
# Return the associated user ID if the token is valid, None otherwise
# Multi-factor authentication
def send_verification_code(user_id):
# Generate and send a verification code to the user
# Store the verification code in the database
def verify_verification_code(user_id, code):
# Check if the provided code matches the one stored in the database
# Return True if the code is valid, False otherwise
User Authorization
Managing user permissions ensures that individuals access only what they’re allowed to, maintaining data security. For example, administrative users may access more sensitive data than regular users.
Here’s a Python code sample of implementing User Authorization:
# Role-based access control
def check_user_permission(user_id, resource_id):
# Query the database to check if the user has permission to access the resource
# Return True if the user has permission, False otherwise
# Attribute-based access control
def check_user_access(user_id, resource_id):
# Query the database to retrieve the user's attributes and resource attributes
# Apply access control policies based on the attributes
# Return True if the user has access, False otherwise
Data Encryption
Protecting data in transit and at rest through encryption safeguards it from unauthorized access. Using robust algorithms like AES is a common practice.
Here’s an example of Data Encryption in Python:
import hashlib
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
# Encrypt data
def encrypt_data(data, key):
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
encrypted_data = cipher.encrypt(data)
return encrypted_data
# Decrypt data
def decrypt_data(encrypted_data, key):
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
decrypted_data = cipher.decrypt(encrypted_data)
return decrypted_data
Secure Communication Protocols
Utilizing HTTPS and TLS ensures encrypted and secure data transmission, especially when handling sensitive user information.
Here’s an example of a Secure Communication Protocol implemented in Python:
import requests
# Make a secure HTTPS request
response = requests.get('<https://example.com>')
# Use TLS/SSL certificates for secure communication
app.run(ssl_context="adhoc")
Secure Storage and Data Handling
Encrypting stored data and employing secure storage technologies are necessary for maintaining data confidentiality.
Here’s an example of Secure Storage and Data Handling in Python:
import bcrypt
# Hash passwords for secure storage
def hash_password(password):
hashed_password = bcrypt.hashpw(password.encode('utf-8'), bcrypt.gensalt())
return hashed_password
# Verify hashed passwords
def verify_password(password, hashed_password):
return bcrypt.checkpw(password.encode('utf-8'), hashed_password)
Key Management and Access Controls
Proper management of encryption keys and access credentials prevents unauthorized resource access. Role-based access control is an effective strategy here.
Here’s an example of Key Management and Access Controls in Python:
# Key management
def generate_encryption_key():
# Generate a secure encryption key
# Store the key securely, such as in a key management system or hardware security module
# Access controls
def check_access(user_id, resource_id):
# Query the database to check if the user has access to the resource based on their role or attributes
# Return True if the user has access, False otherwise
Regular Security Testing
Conducting audits and penetration testing helps identify and rectify vulnerabilities. Adhering to industry standards and regulations is also crucial for system security.
Here’s an example of how to perform regular Security Testing in Python:
import unittest
from unittest.mock import patch
from app import app
# Example unit test with mock patching
class APITestCase(unittest.TestCase):
def test_secure_endpoint(self):
with patch('app.authenticate_user') as mock_authenticate:
mock_authenticate.return_value = True
response = app.test_client().get('/secure-endpoint')
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)
self.assertEqual(response.data, b'Success')
Remember to customize and adapt all these code snippets to your specific application’s needs. These examples provide a starting point for implementing the security practices in your back-end development projects.
Stay Informed
Keeping up with the latest security trends and threats enables continuous improvement in security practices.
Security in back-end development involves robust authentication, careful user authorization, data encryption, secure protocols, vigilant storage practices, stringent access controls, ongoing testing, and staying current with security advancements. These measures collectively ensure the creation of secure and trustworthy applications.
Fundamentals of Web Security
In back-end development, a deep understanding of security threats is key to implementing effective measures. Embracing a security-first approach ensures data integrity and confidentiality.
Key security challenges include:
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
Cross-Site Scripting attacks occur when an attacker manages to inject malicious scripts into content that is then served to a user. These scripts execute within the victim’s browser under the guise of a trusted site, potentially stealing cookies, session tokens, or other sensitive information that can be used to impersonate the victim.
Mitigation Strategies:
Sanitizing User Inputs: Ensure that all user-provided data is sanitized, which means filtering out any potentially malicious content before it’s used or displayed on your site.
This often involves stripping out HTML tags or JavaScript from inputs that are not expected to contain such content.
Using Output Encoding: When displaying user-generated content, employ output encoding techniques.
This involves converting special characters into their HTML or URL encoded equivalents so that they are rendered harmless. For example, characters like <, >, and " are converted to <, >, and ", respectively.
SQL Injection
SQL Injection attacks involve inserting or “injecting” a SQL query via the input data from the client to the application. A successful SQL injection exploit can read sensitive data from the database, modify database data, execute administrative operations on the database, and in some cases, issue commands to the operating system.
Mitigation Strategies:
Parameterized Queries: Use parameterized queries (also known as prepared statements) whenever interacting with the database. This approach allows the database to distinguish between code and data, regardless of the input content.
Avoid Direct SQL Query Concatenation: Never build SQL queries by directly concatenating user input with SQL code. This practice is prone to SQL injection because it treats user input as part of the SQL syntax. Always use safe methods provided by your database access libraries to parameterize inputs.
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
Cross-Site Request Forgery is an attack that tricks the victim into executing unwanted actions on a web application in which they’re currently authenticated.
If the victim is a regular user, a successful CSRF attack can force them to perform state-changing requests like transferring funds, changing their email address, and so on. If the victim is an administrative account, CSRF can compromise the entire web application.
Mitigation Strategies:
Use CSRF Tokens: A CSRF token is a unique, secret, unpredictable value that is generated by the server-side application and transmitted to the client in such a way that it is included in a subsequent HTTP request made by the client. When the next request is made, the server checks the submitted token against the one it issued and rejects the request if the values do not match.
SameSite Cookie Attribute: Utilize the SameSite attribute in cookies, which tells the browser to only send the cookie in requests originating from the same domain as the target domain.
This can effectively prevent CSRF attacks by ensuring that authenticated session cookies are not sent along with requests initiated by third-party websites.
Implementing these strategies can significantly enhance the security of web applications by mitigating some of the most common and impactful security vulnerabilities.
Regular security audits and staying updated with the latest trends are crucial for ongoing protection. In Python development, utilizing frameworks like Flask-Security or Django’s authentication features helps in secure user authentication. They offer password hashing, token authentication, and multi-factor authentication support.
Let’s get into each of these security risks in a bit more detail with some code examples.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS):
# Sanitizing user inputs to prevent XSS attacks
def sanitize_input(input_string):
# Remove HTML tags and special characters from the input string
sanitized_string = input_string.replace('<', '<').replace('>', '>')
return sanitized_string
# Using output encoding to prevent XSS attacks
def output_encode(input_string):
# Encode special characters to their HTML entity representation
encoded_string = html.escape(input_string)
return encoded_string
SQL Injection:
import sqlite3
# Using parameterized queries to prevent SQL injection
def get_user(username):
conn = sqlite3.connect('database.db')
cursor = conn.cursor()
query = "SELECT * FROM Users WHERE username = ?"
cursor.execute(query, (username,))
user = cursor.fetchone()
conn.close()
return user
Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF):
from flask import Flask, render_template, request, session
import secrets
app = Flask(__name__)
app.secret_key = secrets.token_hex(16)
@app.route('/login', methods=['POST'])
def login():
# Generate and store a CSRF token in the session
session['csrf_token'] = secrets.token_hex(16)
# Validate the CSRF token sent in the request
if session['csrf_token'] != request.form['csrf_token']:
return "Invalid CSRF token"
# Continue with the login process
return "Login successful"
@app.route('/form', methods=['GET'])
def form():
# Generate a CSRF token and render the form template
csrf_token = secrets.token_hex(16)
return render_template('form.html', csrf_token=csrf_token)
Remember to customize and adapt the code snippets to your specific application’s needs. These examples provide a starting point for implementing security measures against XSS, SQL injection, and CSRF attacks in your back-end development projects.
User Authentication
User authentication is a critical process in ensuring the security of your application. It involves verifying the identity of users before granting them access to protected resources. There are several authentication mechanisms you can implement, such as passwords, tokens, and multi-factor authentication.
For passwords, it is important to enforce strong password policies that require a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Also, consider implementing features like password complexity checks and password expiration to enhance security. An example of a strong password would be “P@ssw0rd123”.
Tokens are another commonly used authentication mechanism. They are unique strings that are generated and issued to users upon successful authentication. Tokens can be stored securely and used for subsequent requests to authenticate the user.
An example of a token-based authentication flow is using JSON Web Tokens (JWT), where a user logs in and receives a token that is included in subsequent requests for authentication.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide additional verification, such as a one-time password sent to their mobile device or a fingerprint scan. Implementing MFA can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access to user accounts.
For example, when a user logs in, they might be prompted to enter a verification code received via SMS in addition to their password.
To ensure secure authentication, consider the following best practices:
- Implement secure storage for passwords and tokens, such as hashing passwords using strong hashing algorithms like bcrypt or Argon2.
- Utilize encryption for transmitting sensitive authentication data, such as using HTTPS for secure communication.
- Regularly review and update authentication mechanisms to address any known vulnerabilities.
Remember, user authentication is a crucial aspect of your application’s security. By implementing robust authentication mechanisms and following best practices, you can protect user accounts and maintain the trust of your users.
User Authentication:
import bcrypt
import jwt
# Password-based authentication
def authenticate_user(username, password):
# Retrieve the user's hashed password from the database
hashed_password = get_hashed_password(username)
# Verify the provided password against the hashed password
if bcrypt.checkpw(password.encode('utf-8'), hashed_password):
return True
else:
return False
# Token-based authentication
def generate_token(user_id):
# Generate a JSON Web Token (JWT) with the user ID as the payload
token = jwt.encode({'user_id': user_id}, 'secret_key', algorithm='HS256')
return token
def verify_token(token):
try:
# Verify and decode the JWT
decoded_token = jwt.decode(token, 'secret_key', algorithms=['HS256'])
user_id = decoded_token['user_id']
return user_id
except jwt.InvalidTokenError:
return None
# Multi-factor authentication
def send_verification_code(user_id):
# Generate and send a verification code to the user
verification_code = generate_verification_code()
store_verification_code(user_id, verification_code)
send_sms(user_id, verification_code)
def verify_verification_code(user_id, code):
# Retrieve the stored verification code for the user
stored_code = get_verification_code(user_id)
# Check if the provided code matches the stored code
if code == stored_code:
return True
else:
return False
Remember to customize and adapt the code snippet to your specific application’s needs. This example provides a starting point for implementing user authentication in your back-end development projects.
User Authorization
Defining user permissions and access levels is a crucial aspect of user authorization. In Python frontend and backend development, you can achieve this by implementing role-based access control (RBAC) or attribute-based access control (ABAC) mechanisms.
With RBAC, you assign roles to users based on their responsibilities or job titles. For example, you may have roles such as “admin,” “manager,” and “user.” Each role has a predefined set of permissions that determine what actions a user with that role can perform. By assigning appropriate roles to users, you can control their access to different parts of the application.
On the other hand, ABAC takes a more fine-grained approach by considering various attributes of the user, the resource being accessed, and the context in which the access request is made. Attributes like user location, time of day, or user department can influence access decisions. For instance, you can define policies that allow only users from a specific department to access certain sensitive data.
To effectively manage user authorization, consider using a well-established authentication and authorization framework like Django’s built-in authentication system or Flask-Security. These frameworks provide convenient methods and decorators to handle user permissions and access control.
Remember, authentication and authorization are distinct but interconnected concepts. While authentication verifies the identity of users, authorization determines what actions they are allowed to perform. Understanding the difference is crucial for building secure and reliable applications.
Example:
In a Python web application, let’s say you have defined three roles: “admin,” “manager,” and “user.”
- The “admin” role has permissions to perform administrative tasks such as creating and managing users, modifying system settings, and accessing sensitive data.
- The “manager” role can perform tasks related to managing projects, assigning tasks to team members, and generating reports.
- The “user” role has limited permissions and can perform basic actions like creating and updating their own profile, viewing project details, and submitting feedback.
By assigning the appropriate role to each user, you ensure that they have access to the necessary features and data based on their responsibilities and level of authority within the application.
Role-based access control (RBAC) example:
# Define roles and their corresponding permissions
ROLES = {
'admin': ['create_user', 'delete_user', 'modify_settings', 'access_sensitive_data'],
'manager': ['manage_projects', 'assign_tasks', 'generate_reports'],
'user': ['update_profile', 'view_project_details', 'submit_feedback']
}
# Check user's role and perform actions based on permissions
def perform_action(user_role, action):
if user_role in ROLES:
if action in ROLES[user_role]:
# Perform the action
print(f"Performing {action} as {user_role}")
else:
print(f"Access denied. {user_role} does not have permission to perform {action}")
else:
print(f"Invalid role: {user_role}")
# Example usage
perform_action('admin', 'create_user') # Performing create_user as admin
perform_action('manager', 'delete_user') # Access denied. manager does not have permission to perform delete_user
perform_action('user', 'update_profile') # Performing update_profile as user
Attribute-based access control (ABAC) example:
# Define user attributes and their values
USER_ATTRIBUTES = {
'user1': {'department': 'HR', 'location': 'office1'},
'user2': {'department': 'IT', 'location': 'office2'},
'user3': {'department': 'Finance', 'location': 'office1'}
}
# Define resource attributes and their values
RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES = {
'resource1': {'department': 'HR'},
'resource2': {'department': 'IT'},
'resource3': {'department': 'Finance'}
}
# Check user's attributes and resource attributes to determine access
def check_access(user_id, resource_id):
if user_id in USER_ATTRIBUTES and resource_id in RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES:
user_attributes = USER_ATTRIBUTES[user_id]
resource_attributes = RESOURCE_ATTRIBUTES[resource_id]
if user_attributes['department'] == resource_attributes['department']:
# Grant access
print(f"Access granted for {user_id} to {resource_id}")
else:
print(f"Access denied. {user_id} does not have access to {resource_id}")
else:
print(f"Invalid user ID or resource ID")
# Example usage
check_access('user1', 'resource1') # Access granted for user1 to resource1
check_access('user2', 'resource3') # Access denied. user2 does not have access to resource3
check_access('user3', 'resource2') # Access denied. user3 does not have access to resource2
Remember to customize and adapt the code snippets to your specific application’s needs. These examples provide a starting point for implementing role-based access control (RBAC) and attribute-based access control (ABAC) mechanisms in your Python backend development projects.
Encryption Techniques
In Python frontend and backend development, encryption plays a crucial role in safeguarding data. There are different types of encryption to consider: in transit, at rest, and end-to-end.
In Transit Encryption
When data is being transmitted between different systems or over a network, it is important to ensure that it is encrypted. This prevents unauthorized access and eavesdropping on sensitive information.
Implementing secure communication protocols like HTTPS and TLS is essential for encrypting data in transit. For example, you can use the requests library in Python to make API calls using HTTPS, ensuring secure transmission of data.
At Rest Encryption
When data is stored in databases or on physical storage devices, it should be encrypted to protect it from unauthorized access. Choosing the right encryption algorithms and implementing them effectively is crucial for ensuring the security of the stored data.
For instance, in Python, you can use libraries like cryptography to encrypt sensitive data before storing it in a database. By encrypting data at rest, even if the storage medium is compromised, the data remains protected.
End-to-End Encryption
End-to-end encryption provides an additional layer of security by ensuring that data remains encrypted throughout its entire journey, from the sender to the recipient. This means that only the intended recipients can decrypt and access the data.
For example, in a messaging application, end-to-end encryption ensures that only the sender and the intended recipient can read the messages, even if they pass through intermediate servers.
Implementing end-to-end encryption requires careful consideration of cryptographic protocols and key management practices.
Choosing the right encryption algorithms and implementing them effectively is crucial for maintaining the security of your application. It is recommended to use widely accepted and tested encryption algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). Also, regularly updating encryption libraries and frameworks to the latest versions helps address any known vulnerabilities.
Remember, encryption is an important aspect of data security in both frontend and backend development. By implementing encryption techniques, you can protect sensitive data and ensure the confidentiality and integrity of your application’s information.
Secure Communication Protocols
In Python frontend and backend development, ensuring secure data transmission is vital to protect sensitive information. Two key practices for achieving this are utilizing HTTPS and TLS.
Use HTTPS
When transmitting data over networks, it is crucial to use HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure). HTTPS encrypts the data being transmitted, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring data integrity.
By implementing HTTPS, you can secure the communication between clients and servers, safeguarding sensitive user information.
For example, in a Python web application, you can configure your server to use HTTPS by obtaining and installing an SSL/TLS certificate.
Protect API Endpoints and Backend Services
It is essential to secure API endpoints and backend services to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Implementing authentication and authorization mechanisms is crucial here.
For instance, in Python backend development, you can use frameworks like Flask or Django to implement token-based authentication, where users are issued tokens upon successful authentication. These tokens are then included in subsequent requests to authenticate the user and grant access to protected endpoints.
For example, in a Python backend application, let’s consider an API endpoint that allows users to retrieve sensitive user data.
To protect this endpoint, you can implement authentication using JWT (JSON Web Tokens). When a user successfully logs in, they receive a JWT that contains their identity and authorization claims. For subsequent requests to the sensitive endpoint, the user includes this JWT in the request headers. The backend server then validates and verifies the token before granting access to the protected data.
By utilizing HTTPS and implementing robust authentication mechanisms, such as token-based authentication, you can ensure secure data transmission and protect API endpoints and backend services in your Python applications.
Remember, adopting these security practices in Python frontend and backend development is crucial for safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining the trust of your users.
Secure Storage and Data Handling
In Python frontend and backend development, ensuring the secure storage of sensitive data and preventing data leaks are critical considerations. By following best practices, you can enhance data integrity and safeguard confidential information.
Best Practices for Storing Sensitive Data
When it comes to storing sensitive data, several best practices can help maintain its security:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting sensitive data before storing it adds an extra layer of protection. Utilize cryptographic algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) to ensure secure storage. For example, in Python, you can use libraries like
cryptographyto implement encryption in your application. - Secure Key Management: Properly managing encryption keys is crucial for data security. Store keys securely using key management systems or hardware security modules (HSMs) to prevent unauthorized access. Maintain a well-defined key rotation policy to minimize the risk of key compromise.
- Access Controls: Implement robust access controls to restrict data access to authorized personnel only. Use role-based access control (RBAC) or attribute-based access control (ABAC) mechanisms to enforce granular permissions. Regularly review and update access control policies to align with changing requirements.
- Secure Backup and Disaster Recovery: Regularly back up sensitive data and store backup copies securely. Test the restoration process to ensure data availability in case of emergencies. Implement disaster recovery strategies to minimize the impact of data breaches or system failures.
Example:
Let’s consider an example in Python backend development. Suppose you are developing a web application that handles sensitive user data, such as personal information. To ensure secure storage, you can employ the following practices:
- Encrypt the sensitive user data using AES encryption before storing it in the database. This ensures that even if the database is compromised, the data remains protected.
- Implement secure key management by using a key management system to securely store and manage encryption keys. This prevents unauthorized access to the keys, enhancing overall data security.
- Apply access controls to restrict data access to authorized users only. For example, implement RBAC to assign different roles to users and grant them permissions based on their responsibilities and level of authority.
- Regularly back up the encrypted data and store the backup copies securely. Test the restoration process to ensure data availability in case of data loss or system failures.
By following these best practices, you can ensure the secure storage of sensitive data in your Python application, minimizing the risk of data leaks and maintaining the confidentiality of user information.
How to prevent data leaks and ensure data integrity
Preventing data leaks and maintaining data integrity are vital aspects of data security. Consider the following practices:
- Input Validation: Validate all user inputs to prevent common vulnerabilities like SQL injection and cross-site scripting (XSS). Implement server-side input validation and sanitize user inputs to mitigate the risk of code injection attacks.
- Secure File Uploads: Implement strict file upload validation to prevent unauthorized execution of malicious files. Validate file types, limit file sizes, and store uploaded files in a secure location to prevent unauthorized access or execution.
- Secure Logging: Log events and errors securely to prevent sensitive information from being exposed. Avoid logging sensitive data like passwords or personally identifiable information (PII). Utilize secure logging frameworks and ensure log files are protected from unauthorized access.
- Secure Configuration: Maintain secure configurations for your application, server, and related components. Disable unnecessary services, apply security patches promptly, and follow security best practices for server and application configurations.
Example:
Let’s illustrate these practices with a Python frontend development example. Suppose you are developing a web application that accepts user inputs and performs database operations.
To prevent data leaks and ensure data integrity, you can adopt the following measures:
- Implement server-side input validation to validate and sanitize user inputs. This prevents common vulnerabilities like SQL injection and helps maintain data integrity.
- Apply strict file upload validation to ensure that only allowed file types and sizes are accepted. Store uploaded files outside the web root directory to prevent unauthorized access and execution.
- Log events and errors securely using a logging framework that supports secure logging practices. Avoid logging sensitive information, and ensure log files are protected from unauthorized access.
- Maintain secure configurations for your application and server. Regularly update and patch software components, disable unnecessary services, and follow security best practices for configurations.
By implementing these practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of data leaks and maintain the integrity of your application’s data in Python frontend development.
Remember, ensuring secure data storage and preventing data leaks are critical for maintaining the trust of your users and protecting sensitive information. By following these best practices, you can enhance data security in your Python frontend and backend development projects.
Here are some code examples that show various ways to protect your Python applications:
User Authorization:
# Role-based access control
def check_user_permission(user_id, resource_id):
# Query the database to check if the user has permission to access the resource
user_role = get_user_role(user_id)
resource_permissions = get_resource_permissions(resource_id)
if user_role in resource_permissions:
return True
else:
return False
# Attribute-based access control
def check_user_access(user_id, resource_id):
# Query the database to retrieve the user's attributes and resource attributes
user_attributes = get_user_attributes(user_id)
resource_attributes = get_resource_attributes(resource_id)
# Apply access control policies based on the attributes
if user_attributes['department'] == resource_attributes['department']:
return True
else:
return False
Data Encryption:
import hashlib
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
# Encrypt data
def encrypt_data(data, key):
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
encrypted_data = cipher.encrypt(data)
return encrypted_data
# Decrypt data
def decrypt_data(encrypted_data, key):
cipher = AES.new(key, AES.MODE_ECB)
decrypted_data = cipher.decrypt(encrypted_data)
return decrypted_data
Secure Communication Protocols:
import requests
# Make a secure HTTPS request
response = requests.get('<https://example.com>')
# Use TLS/SSL certificates for secure communication
app.run(ssl_context="adhoc")
Secure Storage and Data Handling:
import bcrypt
# Hash passwords for secure storage
def hash_password(password):
hashed_password = bcrypt.hashpw(password.encode('utf-8'), bcrypt.gensalt())
return hashed_password
# Verify hashed passwords
def verify_password(password, hashed_password):
return bcrypt.checkpw(password.encode('utf-8'), hashed_password)
Remember to customize and adapt the code snippets to your specific application’s needs. These examples provide a starting point for implementing user authentication, user authorization, data encryption, secure communication protocols, and secure storage and data handling in your back-end development projects.
Key Management and Access Controls
In Python front-end and back-end development, secure key management and robust access control are crucial for data security.
Key management involves storing encryption keys in secure locations like key management systems or hardware security modules (HSMs). Regular key rotation and limiting key access to authorized personnel are also essential. Implement strong authentication, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to access these keys.
For access control, define granular policies based on user roles and responsibilities, using systems like role-based access control (RBAC) or attribute-based access control (ABAC). Regularly update these policies and combine them with strong authentication methods, including passwords, tokens, or MFA, to safeguard sensitive resources.
For instance, in a Python web application handling sensitive user data or patient records, these practices ensure that only authorized users can access and decrypt critical information, maintaining data integrity and user trust.
In summary, managing encryption keys securely and implementing effective access control are fundamental in Python development to protect data and maintain application integrity.
Secure Key Management:
import os
import cryptography
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
# Generate a new encryption key
def generate_key():
key = Fernet.generate_key()
return key
# Store the encryption key securely
def store_key(key):
# Store the key in a key management system or hardware security module (HSM)
# Follow best practices for securing the key storage
# Retrieve the encryption key
def retrieve_key():
# Retrieve the key from the secure storage
key = get_key_from_storage()
return key
# Example usage
key = generate_key()
store_key(key)
key = retrieve_key()
And you can always go back to the examples of Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) above if you need to review those security processes.
Remember to customize and adapt the code snippets to your specific application’s needs. These examples provide a starting point for implementing secure key management and access control mechanisms in your Python back-end development projects.

Becoming a back-end Python developer goes beyond learning Python and its frameworks; it involves showcasing your skills and solving complex issues through a well-crafted portfolio. This subchapter guides you on preparing for a back-end Python developer role, emphasizing the importance of a portfolio that reflects your technical skills and problem-solving capabilities.
Your portfolio is crucial—it demonstrates your expertise, creativity, and commitment to Python back-end development. Choose projects that mirror your career goals and exhibit essential skills like database management, API development, and system integration.
Select projects that challenge you yet are achievable within a realistic timeline. A mix of complex and straightforward projects shows versatility. Projects like a Data Dashboard or IoT Data Processing Service highlight your ability to work with data-centric applications.
Each project is a chance to display your technical skills and innovative approach. Tackling challenges such as developing secure authentication systems or engaging user interfaces can significantly showcase your development capabilities.
How to Create a Python Back-end Portfolio
In Python back-end development, crafting a personal portfolio is crucial. It’s more than just a display of your skills – it’s a showcase of your practical expertise and your ability to solve real-world problems. The projects you choose to include in your portfolio provide tangible proof of your capabilities to future employers or clients. It’s important to remember that you don’t have to excel in every possible project.
When deciding on the right projects to undertake, align them with your career goals and personal interests. Your portfolio should accurately reflect your professional aspirations in Python back-end development.
Start by identifying the skills you want to highlight. Whether it’s database management, API development, or system integration, select projects that emphasize these abilities. For example, if your aim is to work in data-centric roles, projects like a Data Dashboard or an IoT Data Processing Service would be particularly relevant.
Next, consider the complexity and scope of each project. It’s essential to find a balance – challenging yourself is good, but you also want to complete projects in a reasonable time frame. A well-rounded portfolio that includes a mix of both intricate and simpler, well-executed projects can be more impressive than one filled with unfinished, overly ambitious projects.
Additionally, choose projects that genuinely interest you. Your enthusiasm for a project can lead to more dedication and a higher quality final product. If the idea of creating a Real-time Chat Application excites you, pursue it. Your passion can be a driving force in your learning and can result in more creative and engaging projects.
Keep in mind, your portfolio is an evolving element of your professional growth. Begin with one or two projects that align with your professional objectives and personal interests, and expand your portfolio over time. Each project you undertake is a step forward in your Python back-end development career, enhancing your expertise and confidence.
So, take the initiative, select a project, and begin coding. Every line of code you write contributes not just to an application, but to your future in the dynamic field of Python back-end development.
1. Blog Platform
- Skills Demonstrated: Implementing user authentication and designing relational databases not only strengthens your foundation in security and data management but also demonstrates your capability to handle core web functionalities.
- Technical Highlights: Develop user registration and login systems using Django or Flask, highlighting your expertise in handling user data securely. Designing a database schema to manage posts and comments will showcase your proficiency with Django’s ORM or Flask with SQL extensions.
- Additional Features: Enhance your platform with post categorization, robust search functionality, and rich text editing to demonstrate your attention to detail and user experience.
2. E-commerce Website
- Skills Demonstrated: Developing an e-commerce site tests your ability to design complex databases and create APIs, crucial for handling dynamic user interactions and integrating external services.
- Technical Highlights: Build a structured product catalog and order management system, integrating RESTful services for seamless product interactions. Adding payment processing using APIs like Stripe or PayPal illustrates your adeptness in third-party integrations.
- Additional Features: Implement inventory management and user reviews, incorporating recommendation algorithms to display your skills in enhancing user engagement.
3. Social Media API
- Skills Demonstrated: Building a RESTful API for social media sharpens your skills in data modeling and secure authentication, essential for modern web applications.
- Technical Highlights: Develop robust APIs for managing user profiles and interactions. Implement OAuth for secure user authentication, and optimize data queries for efficient performance.
- Additional Features: Incorporate real-time notifications, an intelligent news feed algorithm, and media upload support to elevate your application’s user experience.
4. Task Management Application
- Skills Demonstrated: Creating a task management tool focuses on your ability to implement CRUD operations and manage user sessions, integrating these with a front-end framework for a comprehensive application development experience.
- Technical Highlights: Develop functionalities for task creation, updates, and organization. Securely manage user sessions, showcasing your ability to handle sensitive data. Integrate with front-end frameworks like React or Angular to demonstrate your full-stack development capabilities.
- Additional Features: Add task prioritization, set deadlines, and reminders to demonstrate your proficiency in enhancing user productivity.
5. Real-time Chat Application
- Skills Demonstrated: This project tests your skills in asynchronous programming and handling real-time data, crucial for applications requiring immediate data reflection and interaction.
- Technical Highlights: Implement WebSocket for real-time, bidirectional communication. Efficiently manage concurrent user connections and ensure seamless message synchronization across clients.
- Additional Features: Introduce chat rooms, file sharing, and user status indicators to demonstrate your ability to create feature-rich, interactive applications.
6. Data Dashboard
- Skills Demonstrated: Building a data dashboard allows you to showcase your expertise in data fetching, processing, and visualization — key skills for handling and presenting data insights.
- Technical Highlights: Utilize Python libraries like Pandas for data manipulation and Matplotlib or Plotly for creating interactive visualizations. Efficiently fetch and process data from various sources.
- Additional Features: Implement customizable widgets and user-specific views, demonstrating your ability to create tailored user experiences.
7. Machine Learning Model Deployment
- Skills Demonstrated: Deploying a machine learning model as a web service shows your readiness to delve into the world of AI, highlighting your skills in integrating complex algorithms into practical applications.
- Technical Highlights: Deploy a pre-trained model and develop APIs for user interaction. Focus on scalability and performance, ensuring your application can handle varying loads.
- Additional Features: Add features for model retraining and incorporate user feedback loops, showcasing your commitment to continuous improvement and user-centric design.
8. IoT Data Processing Service
- Skills Demonstrated: This service demonstrates your ability to handle streaming data and process information from IoT devices, a rapidly growing field in technology.
- Technical Highlights: Develop a system to collect, process, and store IoT device data, utilizing cloud platforms like AWS or Azure for scalability and reliability.
- Additional Features: Include real-time data visualization, device management features, and anomaly detection algorithms, showcasing your innovative approach to data handling.
9. Content Management System (CMS)
- Skills Demonstrated: Creating a CMS from scratch tests your abilities in database schema design, user authentication, and implementing role-based access controls — key elements in creating secure and scalable web applications.
- Technical Highlights: Develop a flexible content system with diverse user roles and permissions. Focus on streamlined content creation, editing, and publishing workflows.
- Additional Features: Incorporate plugin or theme support, add SEO tools, and implement content versioning to demonstrate your foresight in creating a versatile and user-friendly system.
10. Online Reservation System
- Skills Demonstrated: Developing an online reservation system showcases your ability to integrate external APIs and handle complex queries, essential for creating applications that interact with various external services.
- Technical Highlights: Build a comprehensive booking and reservation management system. Seamlessly integrate with additional services like payment processing and mapping.
- Additional Features: Implement user recommendation algorithms, reservation reminders, and promotional offers, highlighting your dedication to creating an engaging and user-friendly experience.
The significance of a well-developed portfolio in Python back-end development is immense. It not only showcases your technical skills but also demonstrates your problem-solving capabilities to potential employers or clients. However, remember that quality trumps quantity. It’s more effective to focus on a few projects that align with your career goals and highlight your core competencies.
Projects like a Blog Platform or an E-commerce Website are ideal for demonstrating a range of abilities in Python back-end development. Each project should reflect professional standards, including well-written code and comprehensive documentation. As you grow in your career, keep your portfolio updated with your latest work, ensuring it evolves with industry trends and best practices.
In essence, carefully select projects that showcase your strengths, and let your portfolio narratively represent your professional growth in Python back-end development. It’s your key to unlocking new opportunities in this dynamic field.
Back-end Python Interview Questions
Preparing for a back-end Python developer interview requires a solid grasp of both the technical and soft skills essential for the role. This chapter is designed to arm you with a comprehensive set of questions that cover a wide range of topics, from general programming knowledge and specific Python skills to problem-solving abilities and understanding of back-end technologies.
Whether you’re a seasoned developer or new to back-end development, these questions will help you assess your preparedness and identify areas for improvement.
General and Behavioral Questions
- Can you describe your experience with back-end development?
- How do you stay updated with the latest back-end technologies and trends?
- Describe a challenging back-end project you worked on.
- How do you approach debugging a complex problem?
- Can you discuss a time you improved the performance of a web application?
- How do you ensure the security of your web applications?
- Describe your experience with team collaboration in development projects.
- What’s your process for testing and quality assurance?
- How do you handle tight deadlines and pressure?
- What motivates you in back-end development?
Technical Skills and Coding Questions
- What languages are you most proficient in for back-end development?
- Can you explain RESTful API design?
- What are the differences between SQL and NoSQL databases? When would you use each?
- How do you manage database transactions and prevent data inconsistencies?
- What are some common HTTP methods, and how are they used?
- Explain the concept of MVC architecture.
- How do you optimize database queries?
- What is containerization, and how does it benefit development?
- Describe the process of API authentication and authorization.
- How do you manage cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) in web applications?
Frameworks and Technologies
- What experience do you have with frameworks like Django, Flask, or Express.js?
- How do you handle session management in web applications?
- Can you explain the concept of middleware in web development?
- What is your experience with cloud services like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud?
- How have you used caching mechanisms to improve application performance?
- What are some challenges you have faced using ORM tools?
- Describe your experience with microservices architecture.
- How do you ensure the scalability of your web applications?
- What tools do you use for version control?
- How do you approach mobile backend development differently from web backend?
Problem-Solving and Algorithm Questions
- How would you design a system for handling high traffic loads?
- Describe how you would implement a rate-limiting feature.
- How would you handle data synchronization across different services?
- Describe your approach to implementing a full-text search in a database.
- Can you explain the concept of load balancing and how it works?
- How would you design a notification system for a high-traffic application?
- Discuss how you would secure sensitive data in transit and at rest.
- How do you approach error handling and logging in back-end applications?
- Describe a time when you had to refactor code for better efficiency.
- How do you handle database schema migrations?
Specific Technologies/Concepts Questions
- Explain the concept of stateless architecture.
- What is the difference between SOAP and REST APIs?
- How do you implement a WebSocket, and what are its advantages?
- What are some best practices for API versioning?
- How do you handle file uploads in your web applications?
- Describe the process of integrating third-party services via APIs.
- What is OAuth, and how do you implement it?
- How do you handle concurrency issues in a database?
- Explain the role of a reverse proxy in web applications.
- What is the difference between horizontal and vertical scaling?
Scenario-Based Questions
- How would you optimize an application with slow response times?
- Describe how you would scale a database for a growing application.
- How would you troubleshoot a memory leak in an application?
- Imagine a scenario where users report frequent timeouts. How would you investigate?
- Describe how you would handle a security breach in a web application.
- How would you manage data consistency across distributed systems?
- If a service is failing intermittently, how would you go about diagnosing it?
- Explain how you would design a back-end for an e-commerce site.
- Describe the steps you would take to migrate a monolithic application to microservices.
- How would you design a back-end system for real-time data processing?
Advanced Conceptual Questions
- What are idempotent operations, and why are they important?
- Can you explain the concept of eventual consistency?
- Describe the trade-offs of a monolithic vs. microservices architecture.
- What is the CAP theorem, and how does it apply to database systems?
- How do you approach dependency injection in back-end applications?
- Explain the concept of Domain-Driven Design (DDD) in back-end development.
- What are design patterns, and can you give examples of how you’ve used them?
- How does event-driven architecture work in back-end systems?
- Explain the role of service discovery in microservices.
- What are some strategies for dealing with database replication lag?
Performance and Optimization Questions
- How do you monitor the performance of your applications?
- Can you discuss strategies for reducing server load?
- What are some ways to handle high-volume data processing efficiently?
- How do you approach optimizing application boot time?
- What tools do you use for performance profiling?
- Discuss how you would reduce the response time of a database query.
- What strategies can be used to reduce the size of a web application’s payload?
- How do you optimize resource utilization in cloud services?
- What are some common performance bottlenecks in web applications, and how do you address them?
- How do you ensure efficient memory management in your applications?
Collaboration and Workflow Questions
- How do you approach code reviews?
- What’s your experience working in Agile development environments?
- How do you handle merge conflicts in a version control system?
- Describe your experience with Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD).
- How do you prioritize tasks in a fast-paced development environment?
- Describe a time you had to collaborate with front-end developers to solve a problem.
- How do you document your code and API for other developers?
- What strategies do you use to ensure clear communication in a remote team?
- How do you stay aligned with product management and other stakeholders?
- Describe your approach to mentoring or onboarding new team members.
Personal Growth and Learning Questions
- How do you keep your programming skills sharp?
- What’s the last programming book you read, or tech talk you watched?
- How do you approach learning a new programming language or framework?
- Can you share an example of a recent technical challenge and how you solved it?
- What areas of back-end development are you looking to improve in?
- Describe a technical topic you’re passionate about.
- How do you balance work with personal development and learning?
- What’s your experience with open-source projects?
- How do you handle feedback and criticism on your code?
- What goals do you have for your future in back-end development?

As we wrap up this comprehensive exploration of Python back-end development, it’s clear that the journey you’re embarking on is both challenging and rewarding.
Python, with its simplicity, versatility, and powerful libraries, stands as a cornerstone for building robust back-end systems. This guide aimed to equip you with the foundational knowledge, best practices, and practical insights necessary to thrive as a Python back-end developer.
Key Takeaways:
- Python’s Role: You’ve learned that Python is not just versatile but pivotal in back-end development. Its frameworks, like Django, Flask, and FastAPI, enable you to build efficient, scalable applications.
- Database Mastery: Understanding the nuances of SQL and NoSQL databases enhances your ability to manage data effectively, ensuring performance and scalability.
- Security First: Emphasizing security practices, from authentication to encryption, is critical. This ensures the integrity and confidentiality of data, building trust and reliability.
- Practical Portfolio: Developing a portfolio with diverse projects demonstrates your skills and problem-solving capabilities, making you stand out in the job market.
- Interview Preparedness: The detailed set of interview questions prepares you to articulate your knowledge and experience confidently, showcasing your readiness for back-end roles.
Moving Forward:
- Continuous Learning: The field of back-end development is ever-evolving. Stay curious, keep learning, and embrace the changes in technologies and methodologies.
- Community Engagement: Join forums, contribute to open-source projects, and network with professionals. The insights and connections you gain are invaluable for your growth and career advancement.
- Practical Application: Apply what you’ve learned in real-world scenarios. Whether through personal projects, freelancing, or in your job, hands-on experience solidifies your skills and opens up new opportunities.
- Mentorship and Sharing: As you grow, seek mentorship from experienced developers. Similarly, share your knowledge with those who are starting their journey. Teaching is a powerful way to reinforce your own learning and contribute to the community.
Embarking on your career as a Python back-end developer is a journey of continuous growth, innovation, and discovery. With the skills and knowledge you’ve acquired, you’re well-equipped to tackle the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. Embrace the journey with confidence, passion, and a willingness to explore new horizons in the dynamic world of Python back-end development.
Resources
Kickstart your journey in technology with our specialized program that dives into Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning. This initiative is crafted to build your programming expertise, supplemented with dedicated mentorship and career guidance to pave your way in the tech industry.
To enrich your learning experience, here’s a helpful selection of targeted resources:
For access to these resources and detailed information about our program, visit LunarTech’s website. Embark on your tech career path with the right tools and support from LunarTech.
Connect with Me:
About the Author
I’m Vahe Aslanyan, specializing in the world of computer science, data science, and artificial intelligence. Explore my work at vaheaslanyan.com. My expertise encompasses robust full-stack development and the strategic enhancement of AI products, with a focus on inventive problem-solving.
Vahe Aslanyan – Crafting Code, Shaping Futures
Dive into Vahe Aslanyan’s digital world, where each endeavor offers new insights and every hurdle paves the way for growth.

My experience includes spearheading the launch of a prestigious data science bootcamp, an endeavor that put me at the forefront of industry innovation. I’ve consistently aimed to revolutionize technical education, striving to set a new, universal standard.
As we close this handbook, I extend my sincere thanks for your focused engagement. Imparting my professional insights through this book has been a journey of professional reflection. Your participation has been invaluable. I anticipate these shared experiences will significantly contribute to your growth in the dynamic field of technology.
[ad_2]
Source link
